Acting now for a sustainable,
low-carbon future

Climate change, resulting at least in part from a surge in the use of fossil fuels and the global warming it has caused, is a serious problem that affects the entire world. Samsung Electronics has acknowledged the reality of the crisis and is therefore continuing efforts on multiple fronts. These include developing highly energy-efficient products, installing equipment with minimum greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, and harnessing new and renewable energy.
2020 KPI: Climate Change
Intensity-based GHG Emissions
for Global Worksites

Cumulative Greenhouse Gas Reduction
in Product Use Phase

We are focused on responding to the climate change crisis
The Greenhouse Gas Council is held four times a year to set the agenda for combating climate change and to review performance. Participants share the latest information on climate change, set detailed action plans, and review their achievements for the quarter. Samsung Electronics has established a systematic management process, as shown below, in order to minimise greenhouse gas emissions throughout the entire lifecycle of our products, including production, distribution and use.
Strategies and Action Plans to Cope with Climate Change

· Operating F-Gas reduction equipment in semiconductor manufacturing process
· Managing energy reduction projects, improving energy efficiency

· Setting up energy management systems at all worksites and maintaining certifications (since 2013)
· Managing each worksite’s energy costs and indicators

· Developing and launching highly energy-efficient products

· Managing GHG emissions in product logistics, business trips, etc. (since 2009)

· Monitoring suppliers’ GHG emissions (since 2012)
We are expanding our emissions management at all levels
Problem solving requires accurate information. To precisely measure and manage our greenhouse gas emissions, we have categorised them into three scopes which are defined by the GHG Protocol based on their proximity to business and operation. Locating the exact point of emission at each level is the basis for managing greenhouse gases in the optimal way.Scope 1 refers to greenhouse gases emitted when products are manufactured at Samsung Electronics’ worksites, while Scope 2 indirect emissions are associated with worksites’ energy purchases to generate electricity and steam. Scope 3 covers non-worksite emissions, such as those from logistics activities, business trips, our supply chain, and the use of our products. We use this analysis to systematically manage all emissions, whether direct or indirect, from our worksites, use of products and our suppliers.

· Monthly analysis of global worksite emissions based on GHG management system
· Installed GHG decomposition equipment in semiconductor processing, with a decomposition rate of 90% and higher
· Installed high-efficiency equipment and converted indoor lighting to LED at global worksites

· Achieved 39 tasks to improve energy efficiency in logistics related areas
· Identified potential GHG reductions of 4,920 tons CO2e at major suppliers
· Reduced overseas business travel by 12% using alternatives such as video conferencing, etc.
· Improved product energy efficiency by 49% in 2016 compared to 2008c

in the Product Use Phase
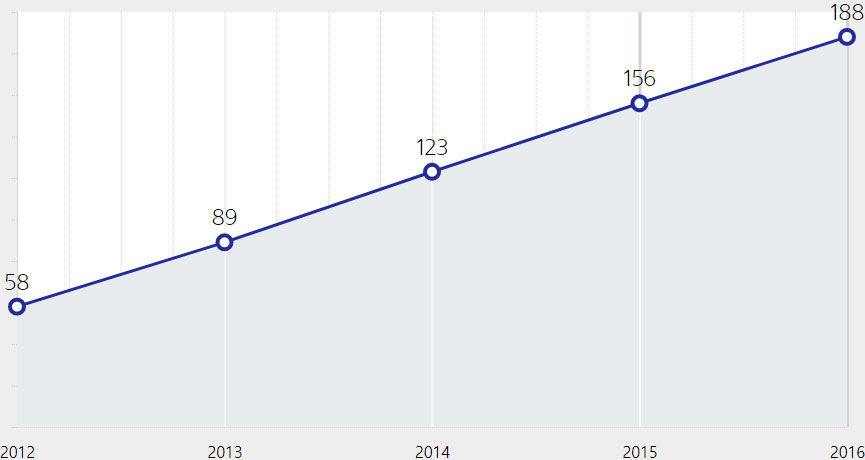
for the last two years.

* Unit: Million tCO2
* Scope of data collection: Eight major product categories(mobile phones, notebooks, TVs, monitors, refrigerators, washers, air conditioners, and printers)
* Accumulated since 2009
We use advanced technology to improve energy efficiency
Samsung Electronics’ advanced technology continues to evolve in the pursuit of an eco-conscious and convenient lifestyle. Samsung Electronics is dedicated to the development of highly energy-efficient products and process technologies to reduce the emission of greenhouse gases during product manufacturing and use. In 2016, we were able to improve our energy efficiency by 49% compared to 2008. These improvements resulted in less energy used, lower costs for consumers and lower greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, we are committed to developing eco-conscious technologies and applying them to our products to fundamentally reduce our impact on global warming.
One example is our refrigerators, which use an eco-conscious refrigerant. Historically, the main cause of ozone depletion has been the use of chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) as a refrigerant. As an alternative to CFCs, an eco-conscious refrigerant called R134 was developed, but there were technical problems in using it in large household refrigerators, so it was only used in smaller models. After a series of studies and experiments, Samsung Electronics successfully applied our technology to enable the use of a refrigerant called R600a, which has a much smaller impact on global warming, compared to large refrigerators. Thanks to these efforts, 20 of our latest refrigerator models were recognised by the US EPA as “ENERGY STAR Most Efficient” in 2017.

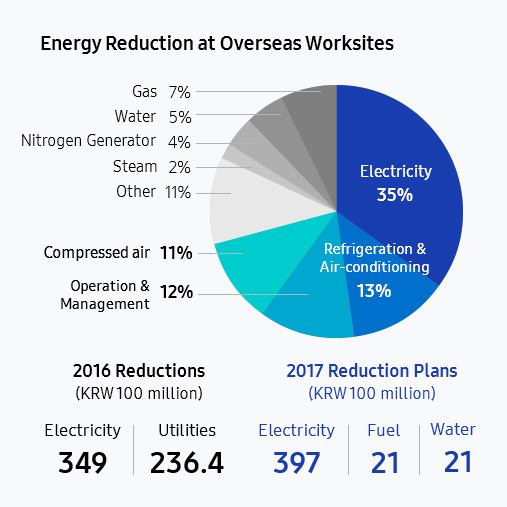
Greater product output requires new manufacturing facilities, which in turn uses more energy on a larger scale. To reduce energy use in the manufacturing phase, Samsung Electronics has been formulating 24 energy-reducing operations standards. In addition, for new worksites, we have developed energy-reducing technologies customised to each worksite and applied them from the process design phase, thereby improving energy efficiency. As a result, in 2016, we were able to achieve energy-use reductions worth a total of KRW 58.5 billion, including electricity and utilities.


We are continuously expanding the use of renewable energy
In 2016, Samsung Electronics’ use of renewable energy increased almost twofold from the previous year and close to six-fold compared to 2014. We have also diversified our sources of new and renewable energy to include solar, wind, and hydropower. In addition, when constructing new buildings, we installed equipment to ensure the use of a certain proportion of renewable energy. At our worksites, we have also been promoting the use of renewable energy in streetlights, transportation and cafeterias. Moreover, in countries with well-established power-purchasing systems, we have been increasing our procurement of renewable energy.
Renewable energy use at global worksites

New and renewable energy use

We are conducting research and projects to adjust to climate change
To find ways as a company to respond and overcome changes in the climate, since 2015 we have been conducting a joint study titled CSR Activities to Adjust to Climate Change. Together with the Graduate School of Environmental Studies at Seoul National University, our researchers have taken on assignments under three themes: access to drinking water, energy-efficient housing and climate change education.
As a part of the drinking water project, we installed semi-permanent drinking water facilities at 10 locations in Vietnam that have struggled to secure a stable supply of potable water. As a result, local residents no longer worry about access to water, a substance vital to life even during the most serious drought.
Meanwhile, our Housing Renovation Projects for the underprivileged have been upgraded to what we call the Housing Energy Efficiency Improvement Construction Project. This project provides households with a living environment that saves energy and insulates them from hot summers and cold winters at a low cost. The pilot project in 2016, involving 10 households, reduced the average annual energy use per household by half and thus cut energy costs for the underprivileged. Beyond the economic gains, it contributed to greenhouse gas reductions of 8.6 tons CO2e per year.
Lastly, at Samsung Smart Schools, we are developing specialized educational content on climate change for both teachers and students. In 2017, using these materials, we launched pilot education programs on climate change for elementary school students, thereby endeavoring to help future generations realize the seriousness of climate change and the importance of efforts to solve the problem.